Agenda
We plan to understand Django REST Framework ModelSerializer in this post.
This post builds on our introductory post of this series which used Serializer instead of ModelSerializer.
Introductory post dealt with creating the following apis using Serializer.
- An api to create a poll question.
- Api to list questions.
- Api to get question detail.
- Api to edit a question.
- Api to delete a question.
- Api to create choice for a particular question.
- Api to see question detail along with available choices.
- Api to vote for a particular choice of a question.
- Api to see result for a particular question.
We will modify these apis to use ModelSerializer.
Setup
You should have the serializers, urlpatterns and apiviews described in the introductory post. You can see the final code of introductory post here.
Create and List questions
This api is available at POST /api/polls/questions/.
questions_view using Serializer looks like:
@api_view(['GET', 'POST'])
def questions_view(request):
if request.method == 'GET':
questions = Question.objects.all()
serializer = QuestionListPageSerializer(questions, many=True)
return Response(serializer.data)
elif request.method == 'POST':
serializer = QuestionListPageSerializer(data=request.data)
if serializer.is_valid():
question = serializer.save()
return Response(QuestionListPageSerializer(question).data, status=status.HTTP_201_CREATED)
return Response(serializer.errors, status=status.HTTP_400_BAD_REQUEST)
QuestionListPageSerializer is a Serializer subclass.
Till now we used a Serializer subclass to perform data validation and provide primitive representation of model instances. Let’s replace the Serializer with ModelSerializer.
A ModelSerializer is a class provided by DRF which can handle data validation and provide primitive representation of model instances.
Let’s write our ModelSerializer in polls/serializers.py
from rest_framework import serializers
from polls.models import Question
class QuestionSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer):
class Meta:
model = Question
exclude = ()
You should have noticed the interface similarity of the ModelSerializer we wrote above with a ModelForm. A ModelForm needs a Meta, similarly a ModelSerializer needs a Meta too. ModelForm.Meta expects a model attribute, similarly ModelSerializer.Meta expects a model too.
We want the serializer to enforce presence of all Question fields while validating POST data, that’s why we have set exclude attribute to an empty tuple.
We could have used fields attribute instead of exclude.
class QuestionSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer):
class Meta:
model = Question
fields = '__all__'
Let’s use this modelserializer in the view.
@api_view(['GET', 'POST'])
def questions_view(request):
if request.method == 'GET':
questions = Question.objects.all()
serializer = QuestionSerializer(questions, many=True)
return Response(serializer.data)
elif request.method == 'POST':
serializer = QuestionSerializer(data=request.data)
if serializer.is_valid():
question = serializer.save()
return Response(QuestionSerializer(question).data, status=status.HTTP_201_CREATED)
return Response(serializer.errors, status=status.HTTP_400_BAD_REQUEST)
A ModelSerializer provides a method called is_valid() similar to Django ModelForm is_valid(). ModelSerializer.is_valid does validation on POSTed data and can report on errors.
ModelSerializer also provides a default implementation of save(). The default implementation of save() creates a model instance and returns the created instance.
Let’s make a POST request without pub_date.
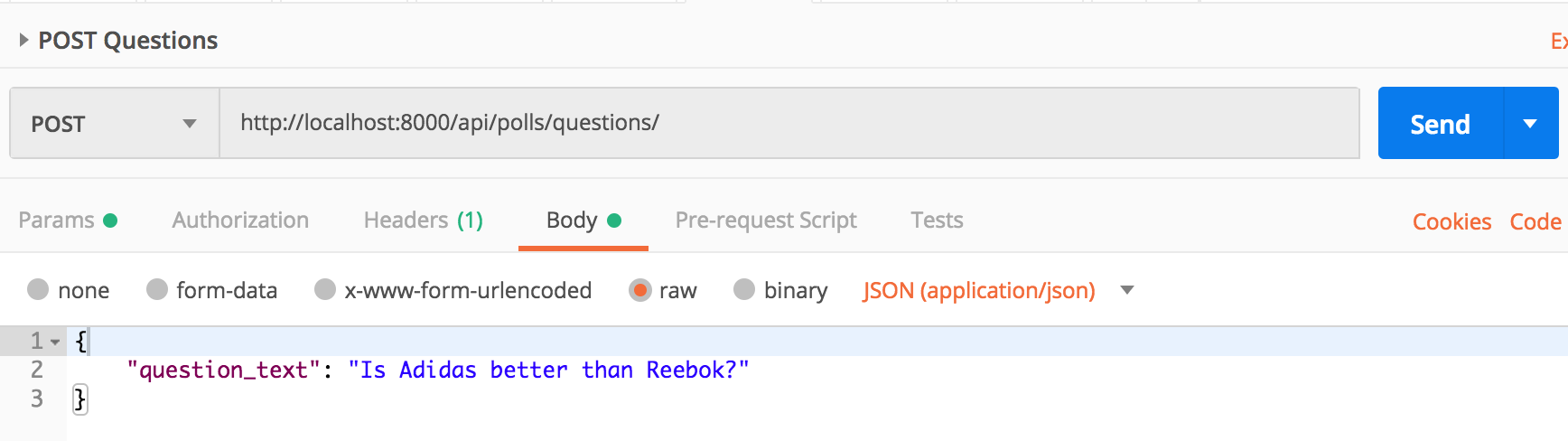
The response should look like:
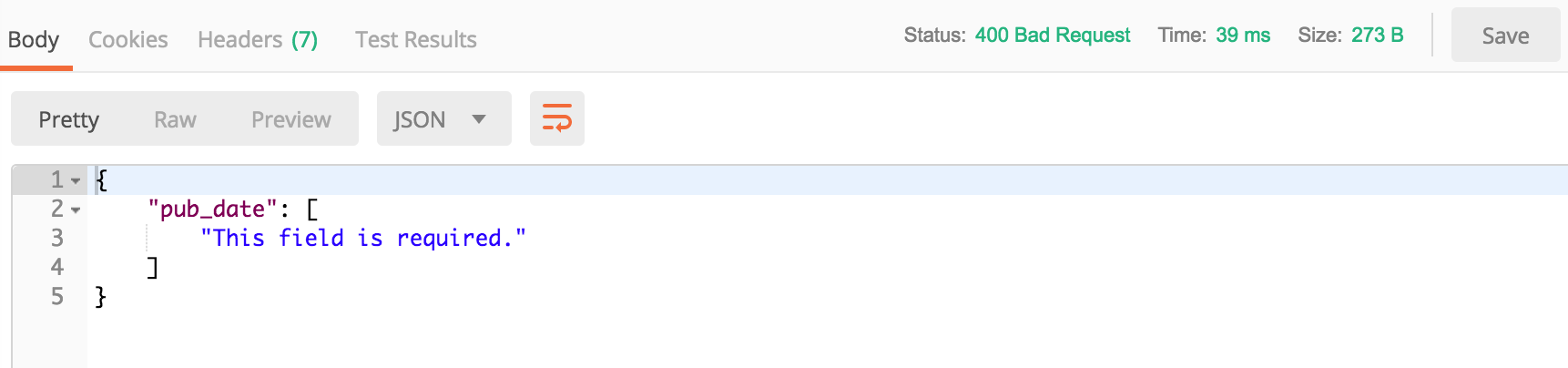
Let’s post with wrong format of pub_date.
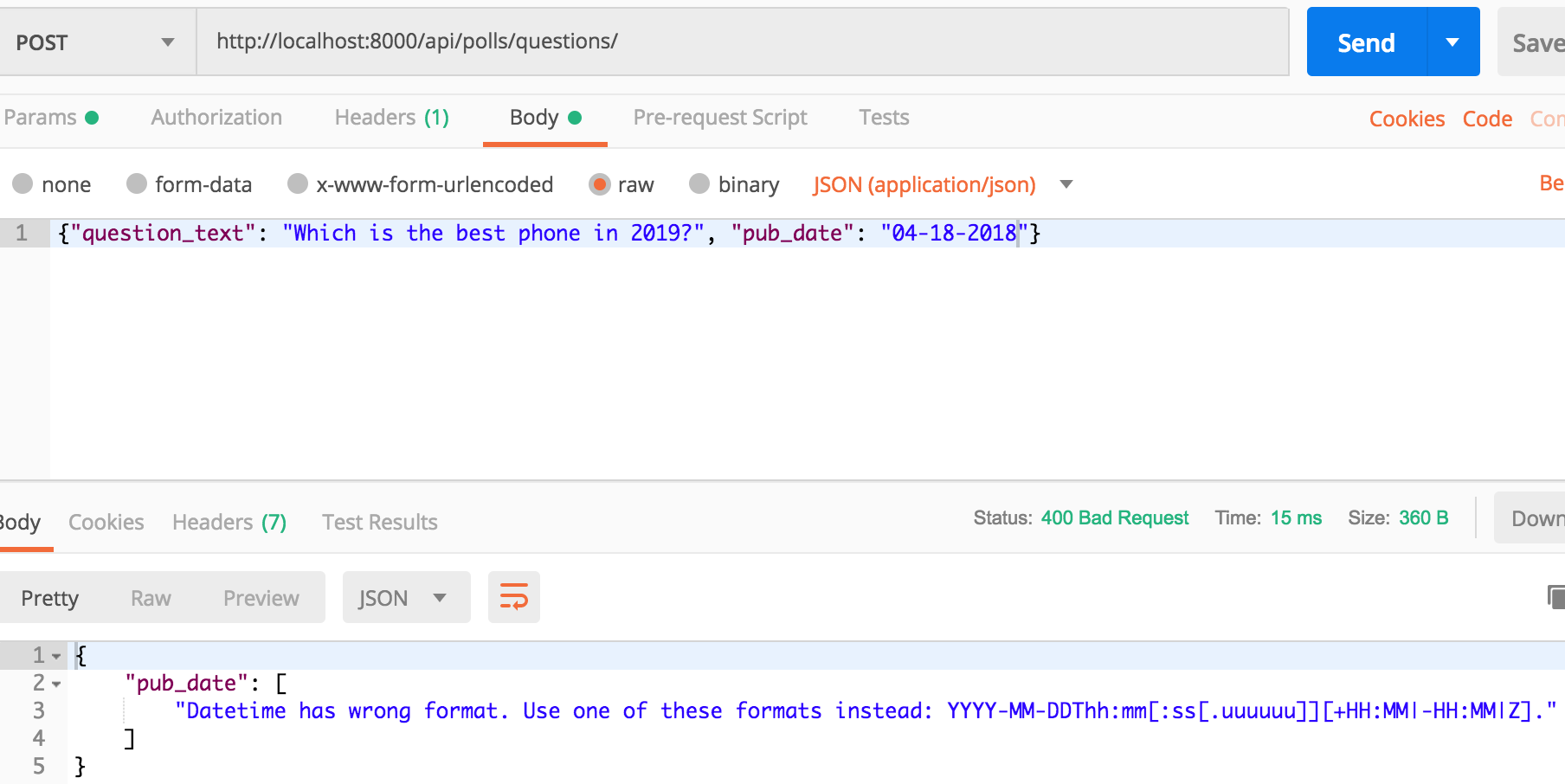
As you should have noticed, the descriptive error messages were provided to us by the modelserializer for free.
POST valid data now:
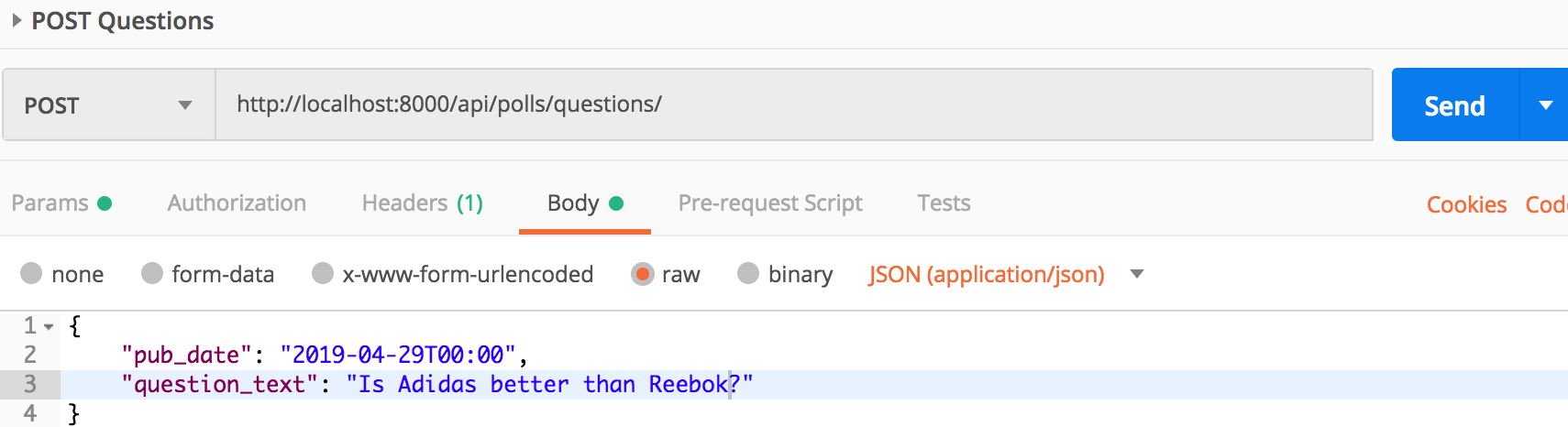
The POST call should have created a Question instance.
In [5]: Question.objects.all()
Out[5]: <QuerySet [<Question: Is Adidas better than Reebok?>]>
POST one more question
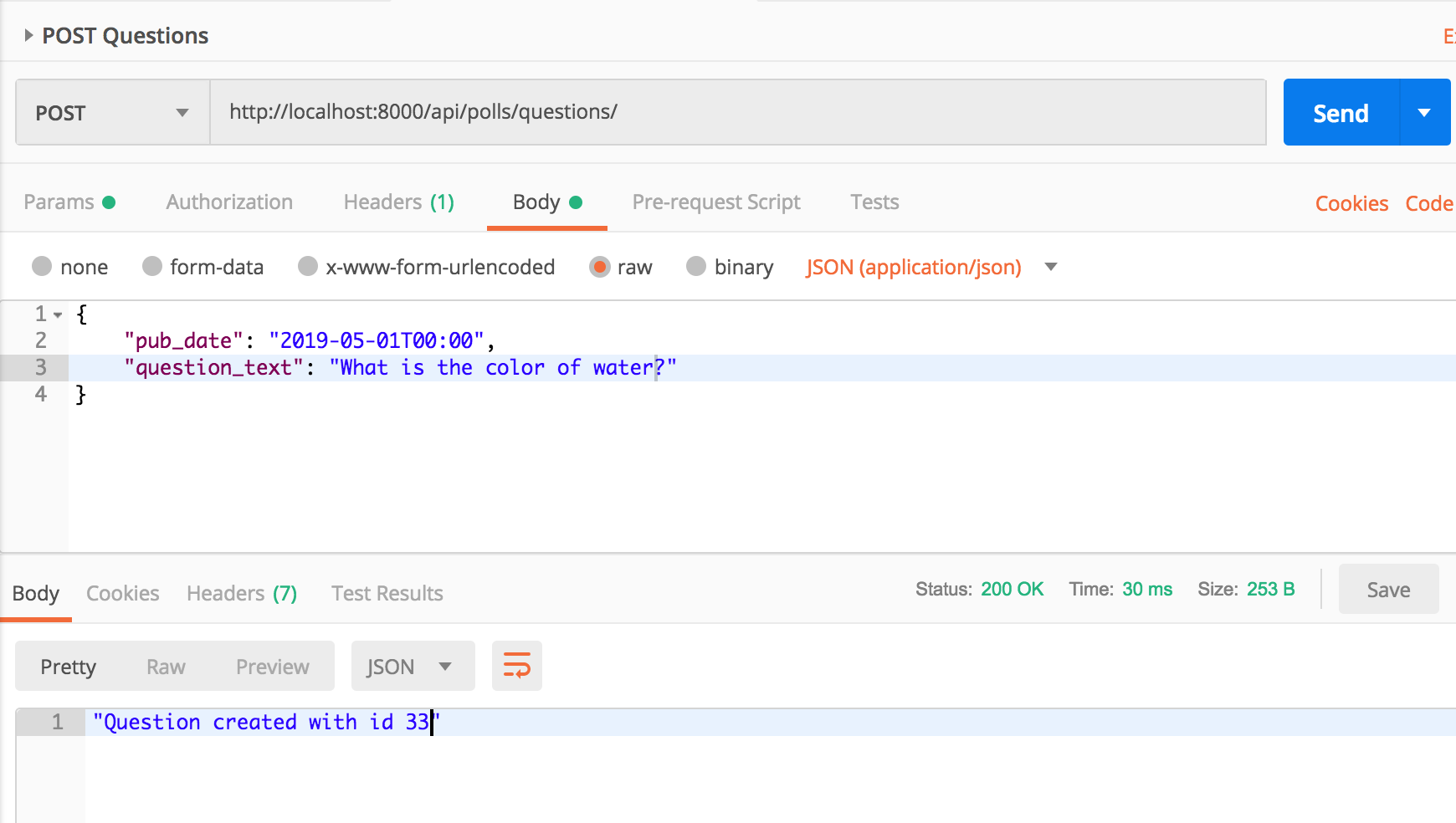
You should have noticed that unlike serializer, we didn’t have to add explicit fields id, pub_date, question_text on modelserializer. Also while using serializer, we had a create() method on serializer which isn’t needed on modelserializer.
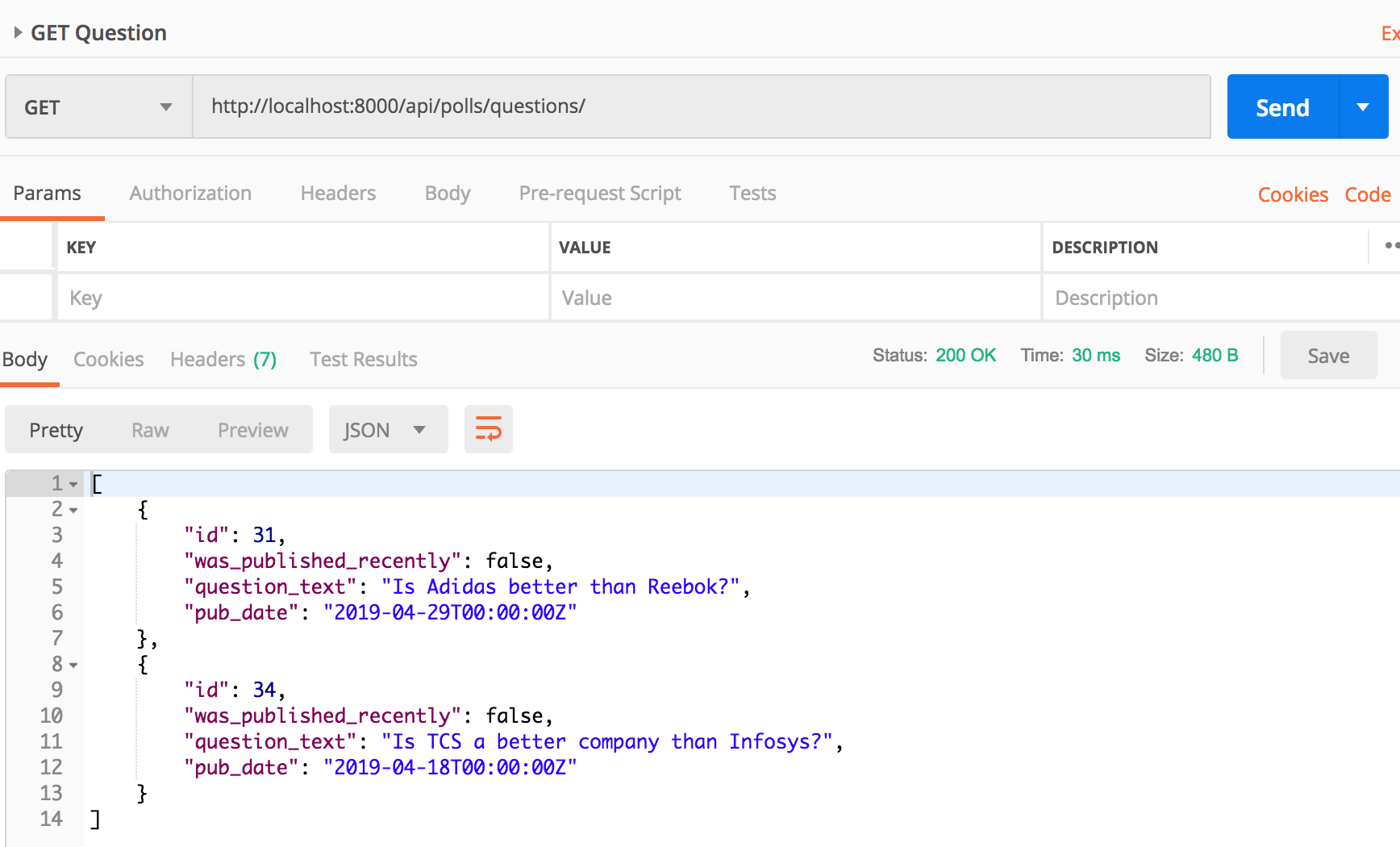
Try GET /api/polls/questions/
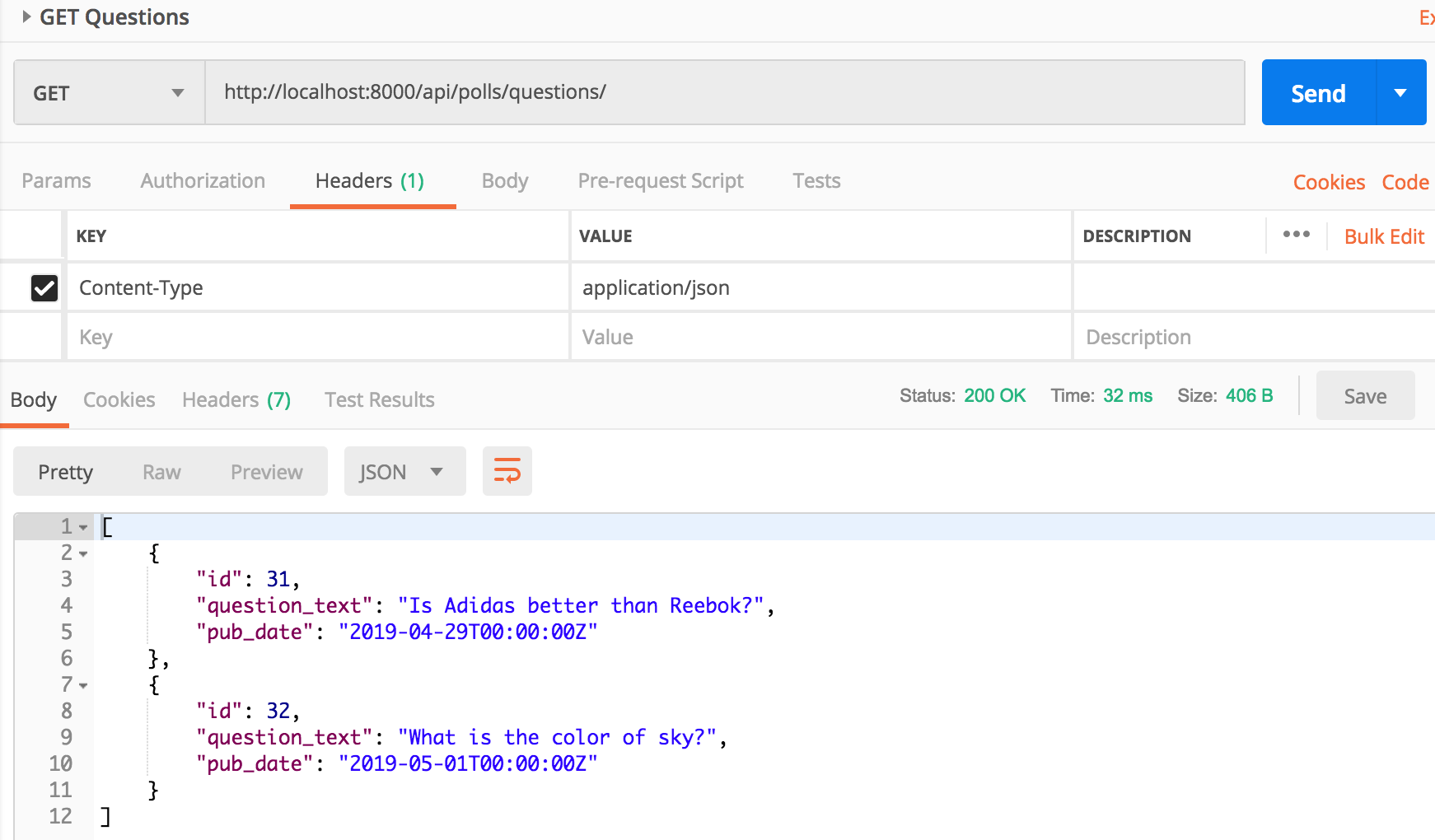
You should see id, pub_date and question_text in the response.
List with derived fields
Question has a method called was_published_recently which returns a boolean. We also want to send was_published_recently for all Questions in GET call.
This will need adding the following line to QuestionSerializer.
was_published_recently = serializers.BooleanField(read_only=True)
We made it read_only because it’s not a model field and so serializer should not be expecting it in POST calls.
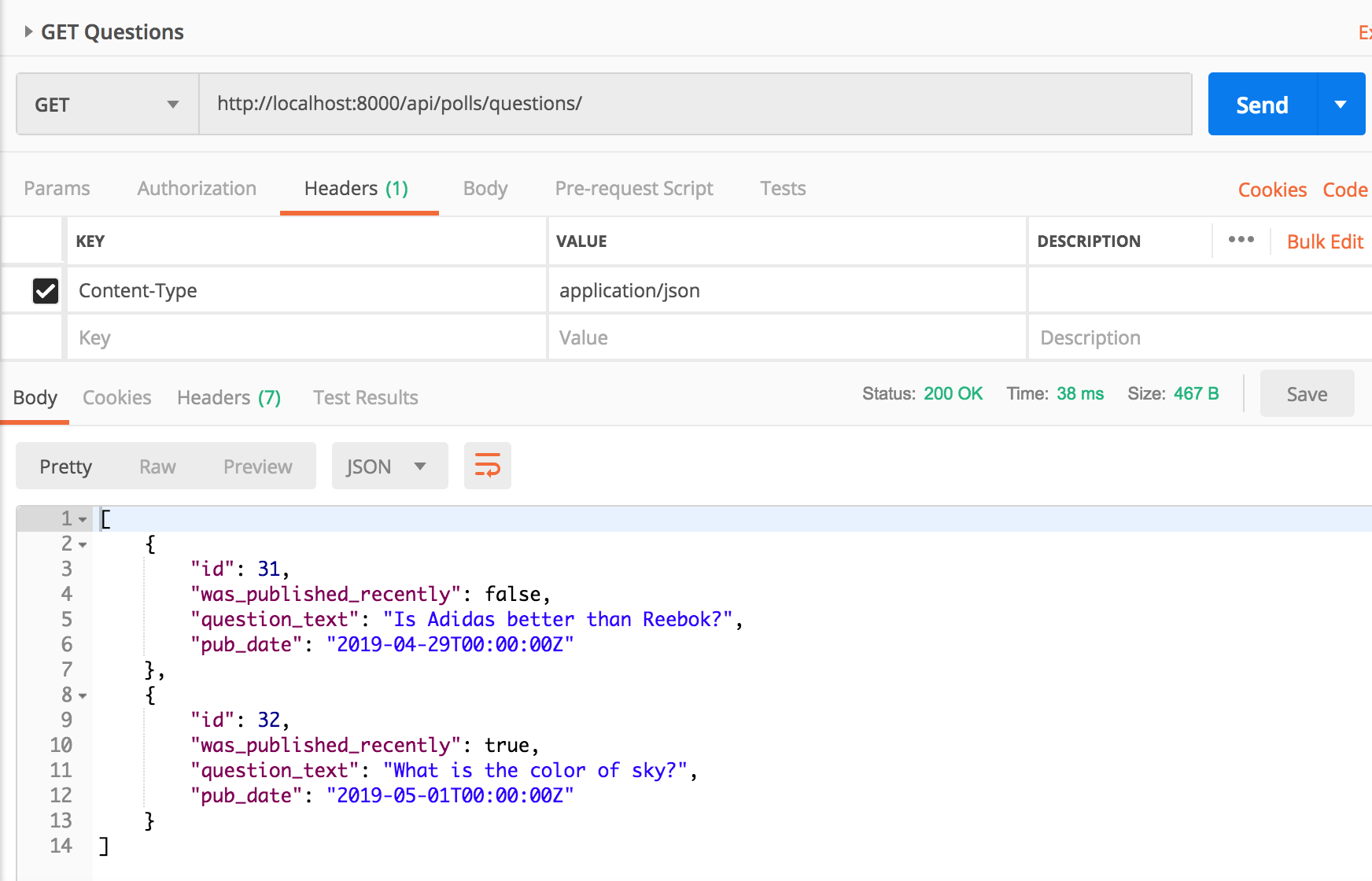
A modelserializer can have explicit fields as in the case of was_published_recently in addition to fields it infers using fields = '__all__'.
Detail of a question
This api is available at GET /api/polls/questions/<question_id>/.
question_detail_view using Serializer looks like:
@api_view(['GET', 'PATCH', 'DELETE'])
def question_detail_view(request, question_id):
question = get_object_or_404(Question, pk=question_id)
if request.method == 'GET':
serializer = QuestionDetailPageSerializer(question)
return Response(serializer.data)
elif request.method == 'PATCH':
serializer = QuestionDetailPageSerializer(question, data=request.data, partial=True)
if serializer.is_valid():
question = serializer.save()
return Response(QuestionDetailPageSerializer(question).data)
return Response(serializer.errors, status=status.HTTP_400_BAD_REQUEST)
elif request.method == 'DELETE':
question.delete()
return Response("Question deleted", status=status.HTTP_204_NO_CONTENT)
Modify the GET handler of this view to use modelserializer QuestionSerializer instead of serializer QuestionDetailPageSerializer.
if request.method == 'GET':
serializer = QuestionSerializer(question)
return Response(serializer.data)
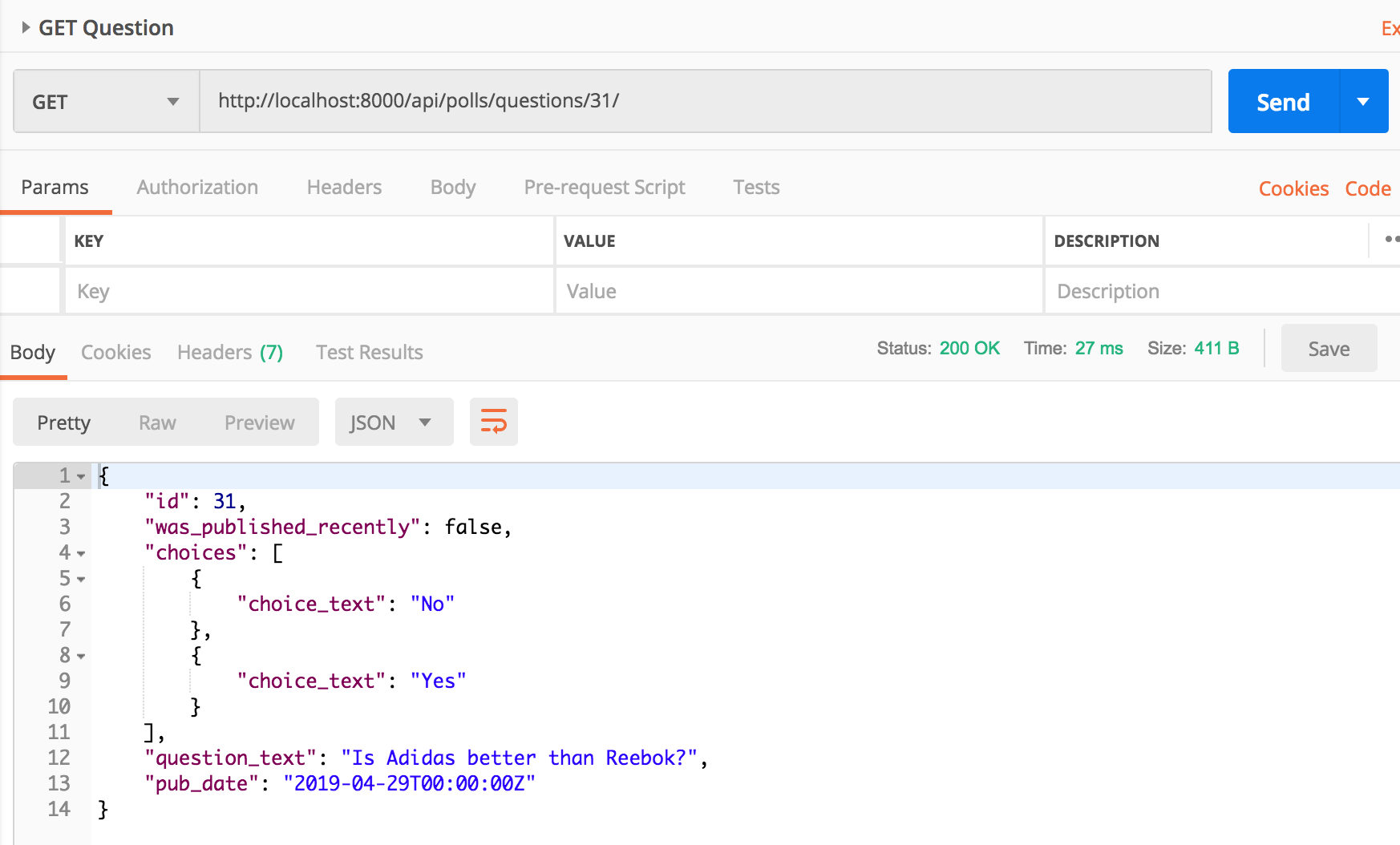
Make a GET request to /api/polls/questions/31/
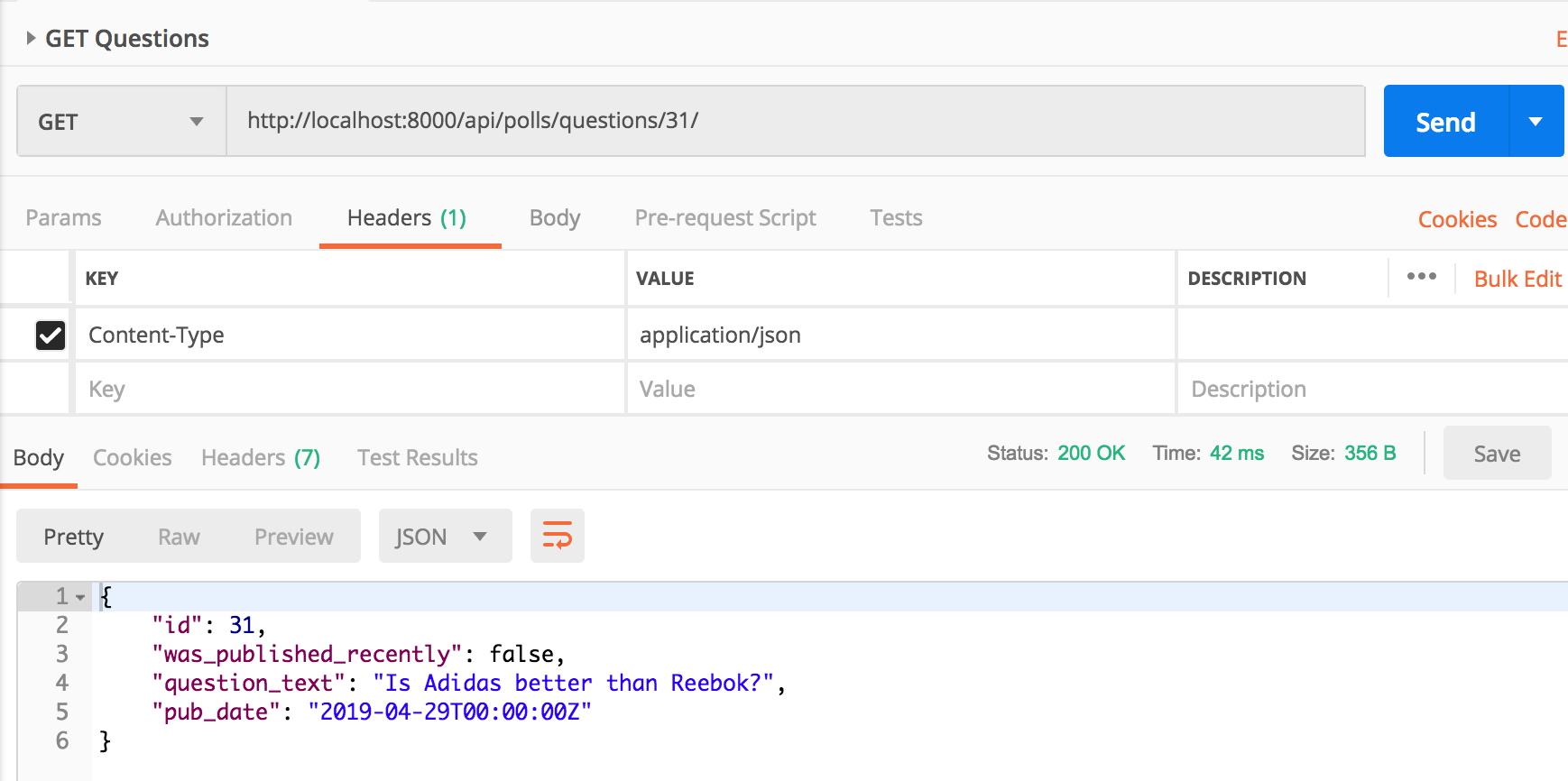
Edit a poll question
The api is available at PATCH /api/polls/questions/<question_id>.
PATCH handler for question_detail_view using Serializer looks like:
elif request.method == 'PATCH':
serializer = QuestionDetailPageSerializer(question, data=request.data, partial=True)
if serializer.is_valid():
question = serializer.save()
return Response(QuestionDetailPageSerializer(question).data)
return Response(serializer.errors, status=status.HTTP_400_BAD_REQUEST)
Modify the PATCH handler of to use modelserializer QuestionSerializer instead of serializer QuestionDetailPageSerializer.
elif request.method == 'PATCH':
serializer = QuestionSerializer(question, data=request.data, partial=True)
if serializer.is_valid():
question = serializer.save()
serializer = QuestionSerializer(question)
return Response(serializer.data)
return Response(serializer.errors, status=status.HTTP_400_BAD_REQUEST)
question_text of Question id 32 is “What is the color of sky?”. Let’s change it to “What is the color of sky? Is it blue?” by making a PATCH request to /api/polls/questions/32/.
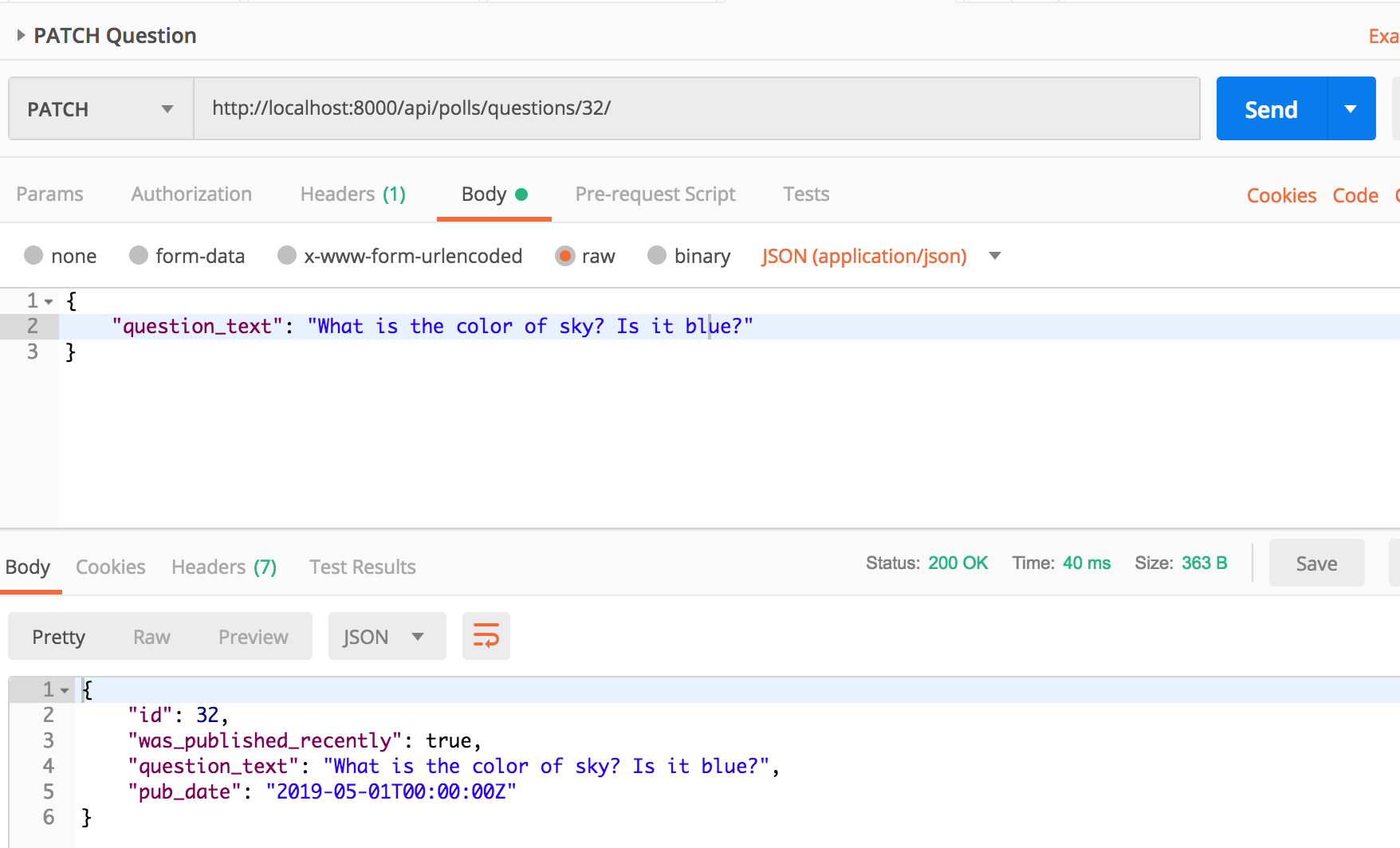
As you should have noticed, earlier the serializer required an update() implementation to handle editing of instance. But our modelserializer provides a default implementation of update() which was used to correctly edit the instance. We didn’t have to add an update implementation for QuestionSerializer.
Delete a poll question
The api is available at DELETE /api/polls/questions/<question_id>.
DELETE handler doesn’t use the serializer so we don’t need to modify the delete code.
elif request.method == 'DELETE':
question.delete()
return Response("Question deleted", status=status.HTTP_204_NO_CONTENT)
Let’s delete the question with id 32.
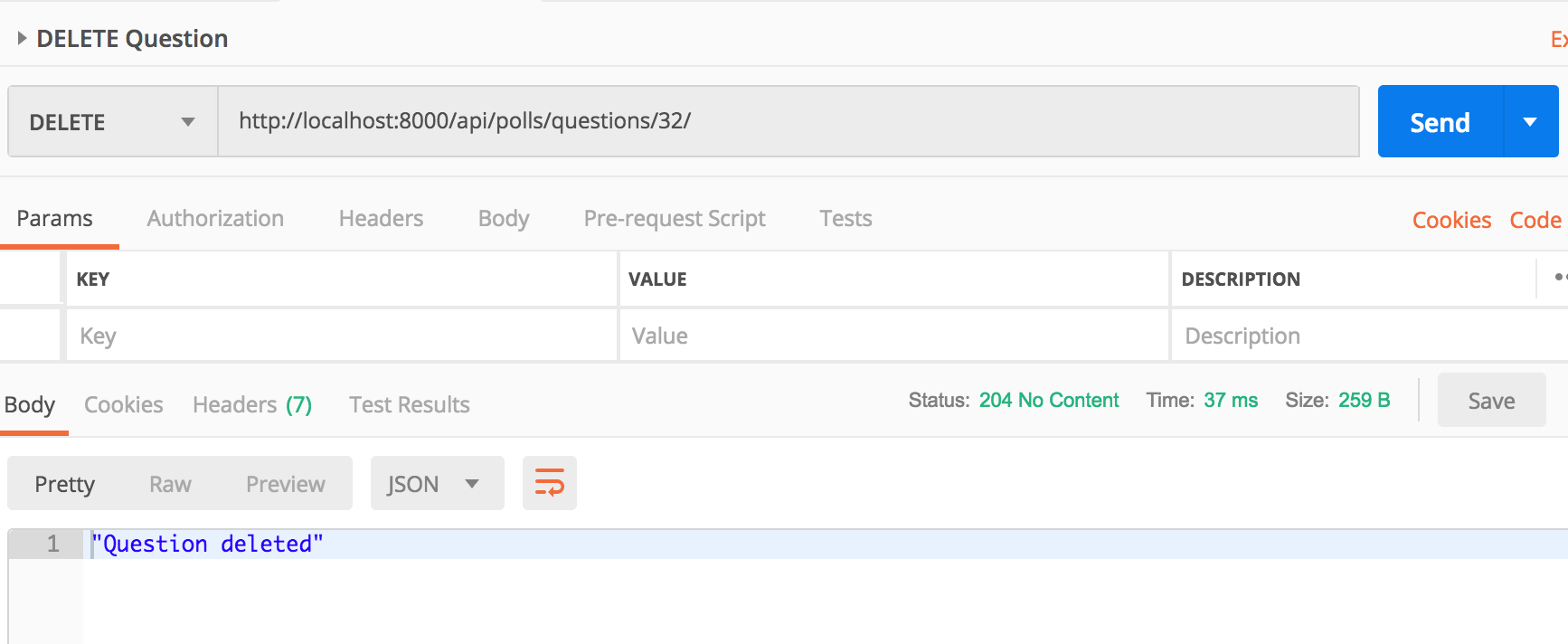
Post a question choice
The api is available at POST /api/polls/questions/<question_id>/choices/.
Serializer subclass ChoiceSerializer looks like:
class ChoiceSerializer(serializers.Serializer):
id = serializers.IntegerField(read_only=True)
choice_text = serializers.CharField(max_length=200)
def create(self, validated_data):
return Choice.objects.create(**validated_data)
Let’s make it a ModelSerializer.
class ChoiceSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer):
class Meta:
model = Choice
fields = ('choice_text',)
We don’t need to modify the apiview since no new serializer was added.
@api_view(['POST'])
def choices_view(request, question_id):
question = get_object_or_404(Question, pk=question_id)
serializer = ChoiceSerializer(data=request.data)
if serializer.is_valid():
choice = serializer.save(question=question)
return Response(ChoiceSerializer(choice).data, status=status.HTTP_201_CREATED)
return Response(serializer.errors, status=status.HTTP_400_BAD_REQUEST)
Let’s make the api call to create a choice for Question id 1.
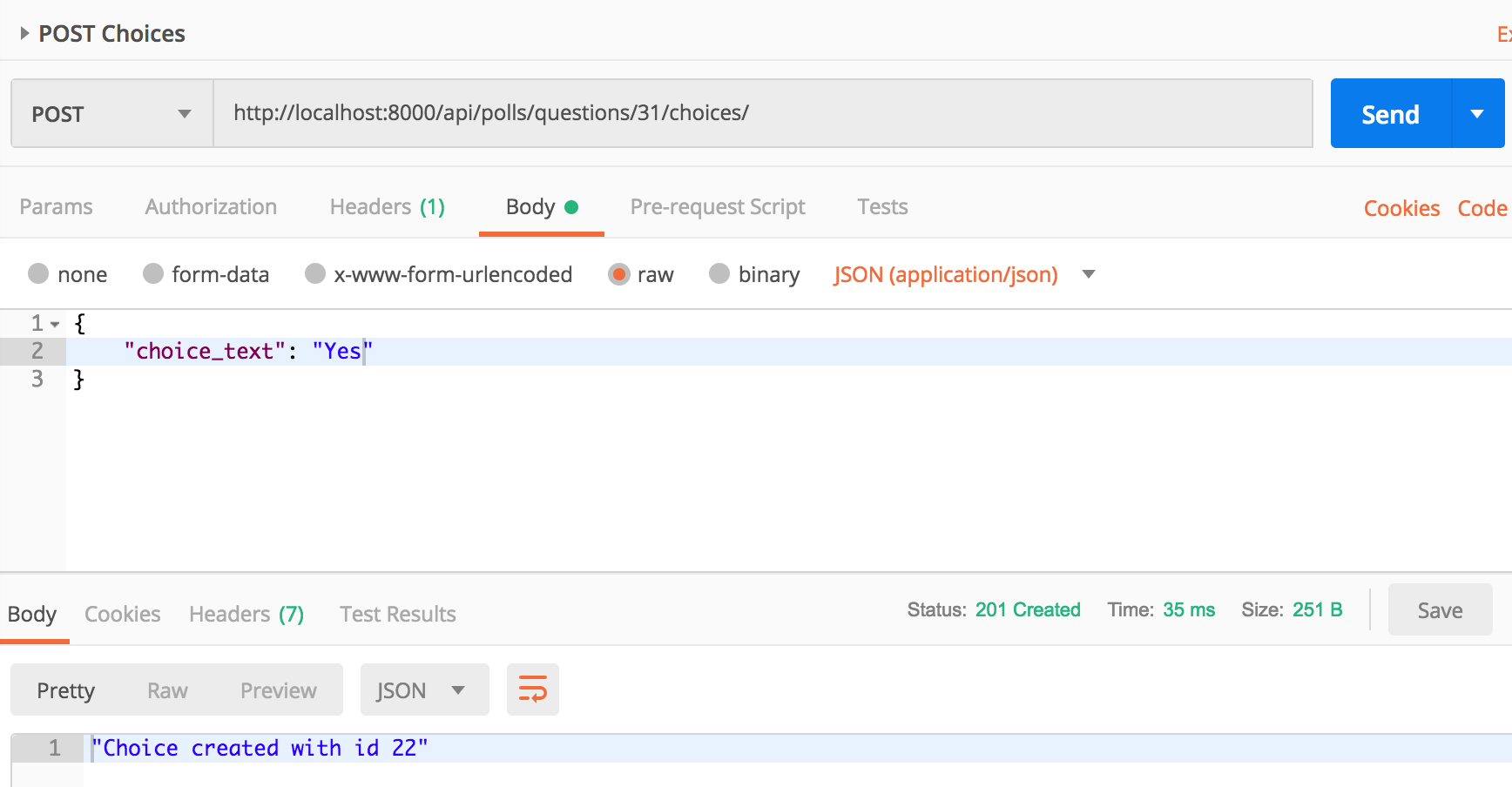
You should have noticed that serializer needed a create() implementation but modelserializer doesn’t need one.
Question detail with choices
We already added an api for question detail which is available at GET /api/polls/questions/<question_id>.
But currently the response for a question doesn’t include the choices for the question. We can get question choices in the api response by modifying the modelserializer and adding a model method.
Add the following model method to Question.
class Question(models.Model):
....
def choices(self):
if not hasattr(self, '_choices'):
self._choices = self.choice_set.all()
return self._choices
Add the following line to QuestionSerializer
choices = ChoiceSerializer(many=True, read_only=True)
Make a GET request for Question detail for question 31 and you should see the choices for question in the api response.
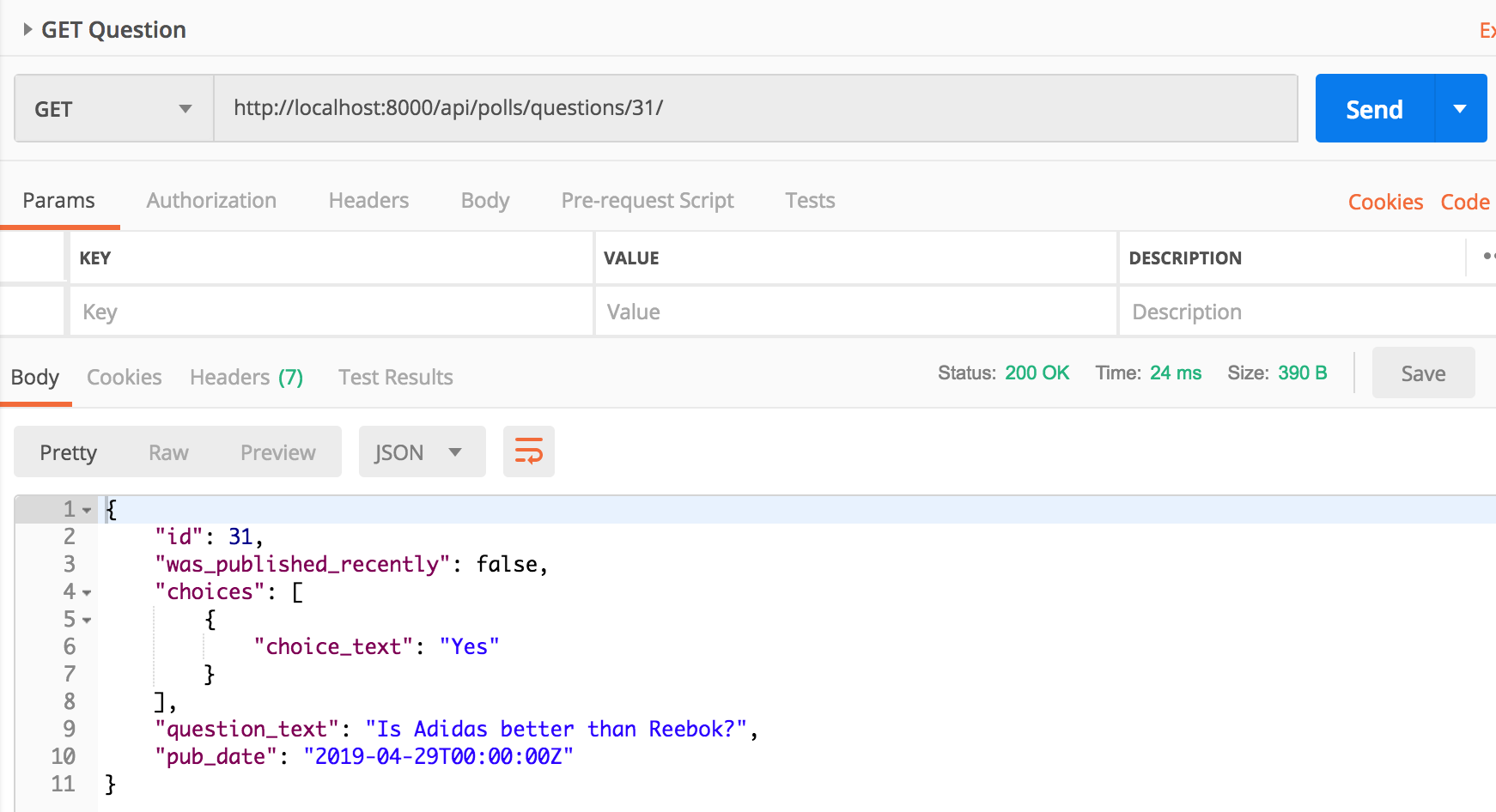
This has a caveat though. This would also include the choices for each question in Question list api. We don’t want choices in Question list api, we only want it in Question detail api.
Let’s do some refactoring to split QuestionSerializer into two classes which are QuestionListPageSerializer and QuestionDetailPageSerializer.
class QuestionListPageSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer):
was_published_recently = serializers.BooleanField(read_only=True)
class Meta:
model = Question
fields = '__all__'
class QuestionDetailPageSerializer(QuestionListPageSerializer):
choices = ChoiceSerializer(many=True, read_only=True)
Let’s also modify the views to use QuestionListPageSerializer in list view and use QuestionDetailPageSerializer in detail view.
@api_view(['GET', 'POST'])
def questions_view(request):
if request.method == 'GET':
questions = Question.objects.all()
serializer = QuestionListPageSerializer(questions, many=True)
return Response(serializer.data)
elif request.method == 'POST':
serializer = QuestionListPageSerializer(data=request.data)
if serializer.is_valid():
question = serializer.save()
serializer = QuestionListPageSerializer(question)
return Response(serializer.data, status=status.HTTP_201_CREATED)
return Response(serializer.errors, status=status.HTTP_400_BAD_REQUEST)
@api_view(['GET', 'PATCH', 'DELETE'])
def question_detail_view(request, question_id):
question = get_object_or_404(Question, pk=question_id)
if request.method == 'GET':
serializer = QuestionDetailPageSerializer(question)
return Response(serializer.data)
elif request.method == 'PATCH':
serializer = QuestionListPageSerializer(question, data=request.data, partial=True)
if serializer.is_valid():
question = serializer.save()
return Response(QuestionListPageSerializer(question).data)
return Response(serializer.errors, status=status.HTTP_400_BAD_REQUEST)
elif request.method == 'DELETE':
question.delete()
return Response("Question deleted", status=status.HTTP_204_NO_CONTENT)
Verify that choices are only returned in Question detail response and that they aren’t returned in Question list response.
Thank you for reading the Agiliq blog. This article was written by Akshar on May 2, 2019 in API , django , drf .
You can subscribe ⚛ to our blog.
We love building amazing apps for web and mobile for our clients. If you are looking for development help, contact us today ✉.
Would you like to download 10+ free Django and Python books? Get them here
