Agenda
DRF provides several generic views. ListCreateAPIView is one among them.
In this post, we will see when ListCreateAPIView should be preferred over vanilla APIView. We will also see several hook points provided by ListCreateAPIView.
Setup
We will use Django polls app as our reference throughout this post. I assume you are familiar with Question and Choice model used in polls app.
Let’s assume we have a class based apiview to create and list questions. The serializer looks like the following:
# polls/serializers.py
class QuestionChoiceSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer):
class Meta:
model = Choice
fields = ('id', 'choice_text')
class QuestionDetailPageSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer):
was_published_recently = serializers.BooleanField(read_only=True)
choice_set = QuestionChoiceSerializer(read_only=True, many=True)
class Meta:
model = Question
fields = '__all__'
The apiview looks like the following:
from rest_framework.views import APIView
class QuestionsView(APIView):
def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
questions = Question.objects.all()
serializer = QuestionDetailPageSerializer(questions, many=True)
return Response(serializer.data)
def post(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
serializer = QuestionDetailPageSerializer(data=request.data)
if serializer.is_valid():
question = serializer.save()
serializer = QuestionDetailPageSerializer(question)
return Response(serializer.data, status=status.HTTP_201_CREATED)
return Response(serializer.errors, status=status.HTTP_400_BAD_REQUEST)
The urlpattern for this apiview is:
# polls/urls.py
path('questions/', apiviews.QuestionsView.as_view(), name='questions_view')
Urlpattern of root URLconf file is:
# mysite/urls.py
path('api/polls/', include('polls.urls'))
The api call to create question looks like:
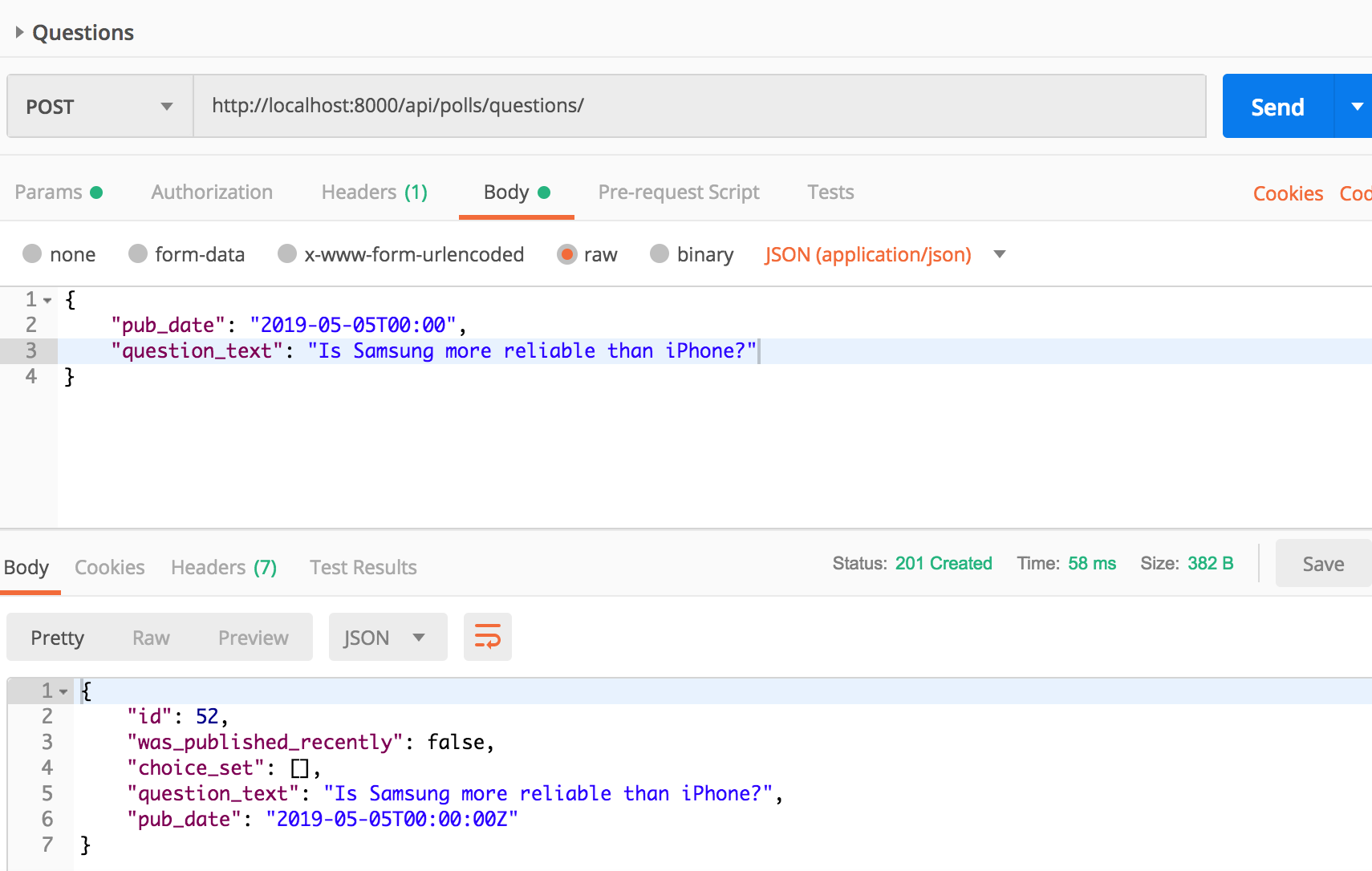
The api call to list questions looks like:
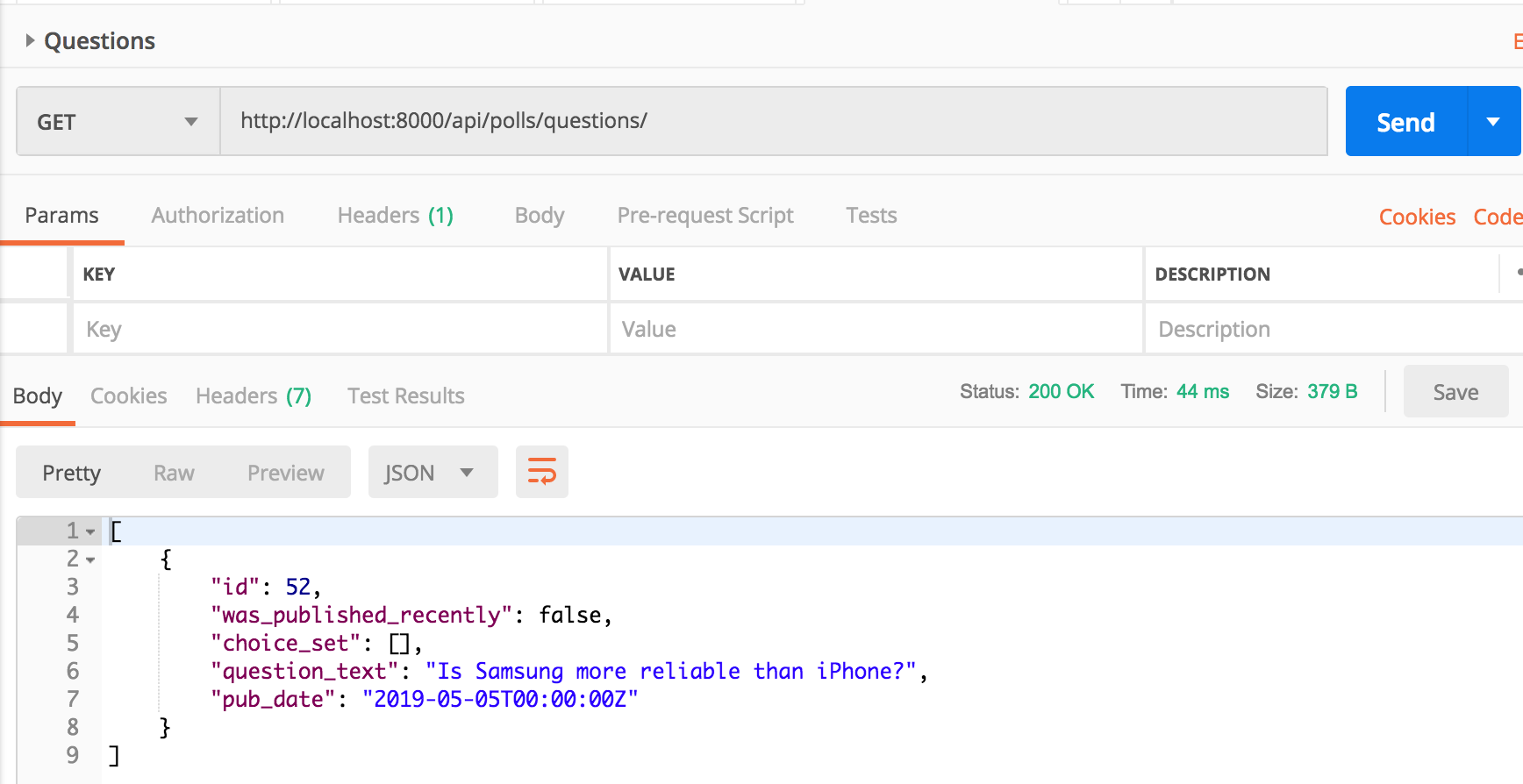
Side Note: Read our detailed post on adding an api layer to Django polls app.
ListCreateAPIView
Our view has a very commonly occuring pattern where we want to create an instance of a model and want to provide representation of all instances of a model. We had to provide a get() and post() implementation to achieve this.
ListCreateAPIView provides a default implementation of get() and post(). It requires two mandatory attributes which are serializer_class and queryset.
Let’s modify the QuestionsView to use ListCreateAPIView.
class QuestionsView(ListCreateAPIView):
queryset = Question.objects.all()
serializer_class = QuestionDetailPageSerializer
Make the api calls for create and list again and your responses should remain unchanged.
In GET calls, the default implementation of ListCreateAPIView.get uses queryset attribute of the class to find the objects which should be serialized and uses serializer_class attribute for serializing.
In POST calls, the default implementation of ListCreateAPIView.post creates an instance of self.serializer_class and validates the created serializer. It then does .save() on the created serializer.
You should appreciate the number of lines of code reduced by using ListCreateAPIView over vanilla APIView.
Suppose we only want to show Questions published in last two days in list question api call. We can use a hook point get_queryset to achieve this.
from django.utils.timezone import now
from datetime import timedelta
class QuestionsView(ListCreateAPIView):
serializer_class = QuestionDetailPageSerializer
def get_queryset(self):
last_two_days = now() - timedelta(days=2)
return Question.objects.filter(pub_date__gt=last_two_days)
Since we overrode get_queryset, so there is no need for queryset attribute on the class.
Now we want to allow creating choices while creating a Question, but we don’t want choices to be visible during listing of questions.
You can split QuestionDetailPageSerializer into two classes.
class QuestionListPageSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer):
was_published_recently = serializers.BooleanField(read_only=True)
class Meta:
model = Question
fields = '__all__'
class QuestionDetailPageSerializer(QuestionListPageSerializer):
choice_set = QuestionChoiceSerializer(many=True)
def create(self, validated_data):
choice_validated_data = validated_data.pop('choice_set')
question = Question.objects.create(**validated_data)
choice_set_serializer = self.fields['choice_set']
for each in choice_validated_data:
each['question'] = question
choices = choice_set_serializer.create(choice_validated_data)
return question
And modify QuestionsView to use QuestionListPageSerializer during listing and QuestionDetailPageSerializer during creation. This would need using hook point get_serializer_class.
class QuestionsView(ListCreateAPIView):
def get_queryset(self):
last_two_days = now() - timedelta(days=2)
return Question.objects.filter(pub_date__gt=last_two_days)
def get_serializer_class(self):
if self.request.method == 'GET':
return QuestionListPageSerializer
else:
return QuestionDetailPageSerializer
Because we overrode get_serializer_class, that’s whey we don’t need to provide class attribute serializer_class.
Make a POST request with choice_set.
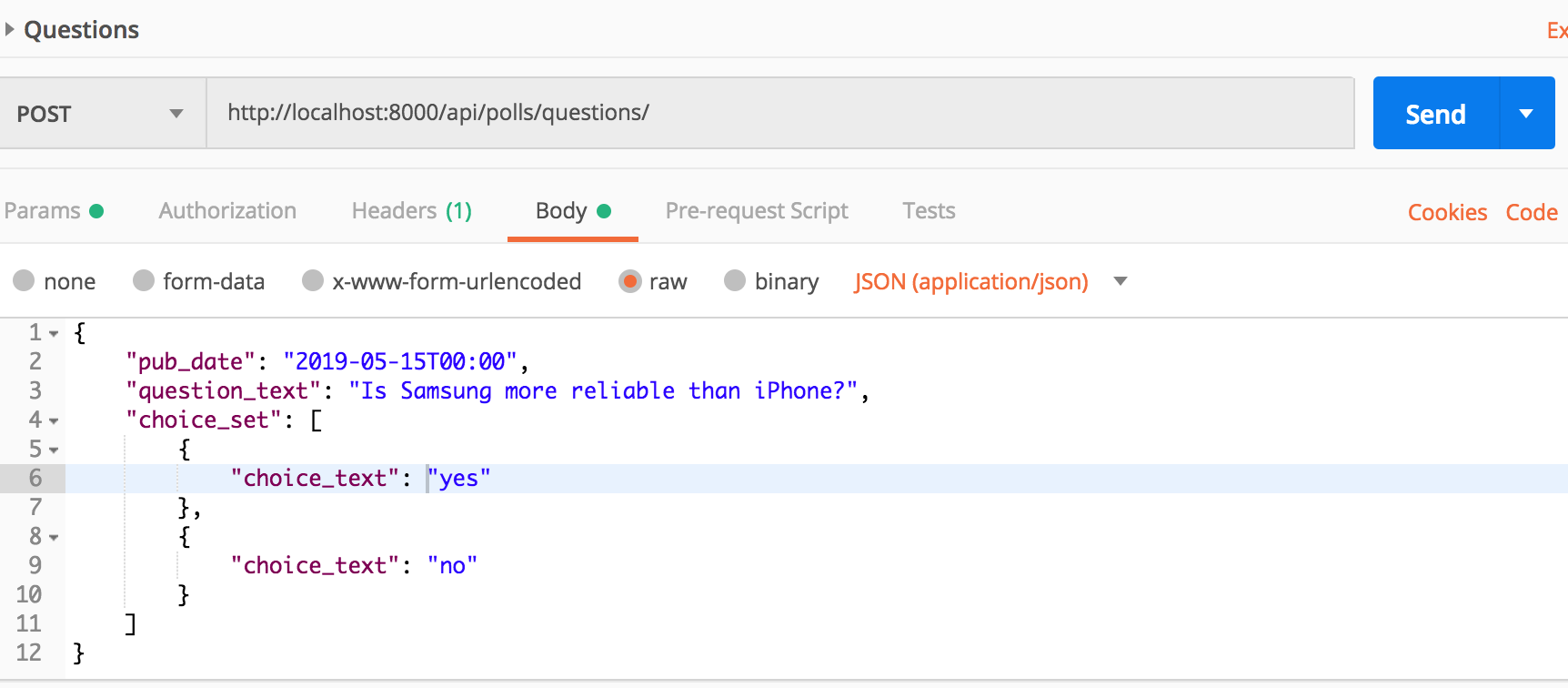
Your GET request will not have choice_set in response because you used QuestionListPageSerializer in GET calls.
Thank you for reading the Agiliq blog. This article was written by Akshar on May 15, 2019 in API , django , drf .
You can subscribe ⚛ to our blog.
We love building amazing apps for web and mobile for our clients. If you are looking for development help, contact us today ✉.
Would you like to download 10+ free Django and Python books? Get them here
